
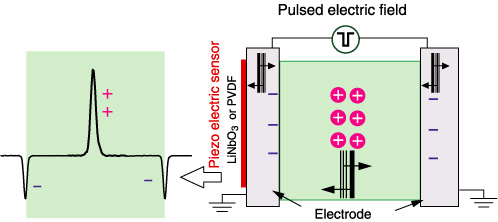
Space charge measurement using the acoustic technique has become a common method for investigating dielectric properties of solid materials. The pulsed electroacoustic (PEA) method has been used for various industrial applications, such as for the evaluation of ion conductive materials. Typical PEA systems can measure space charge profiles in the thickness direction of specimens, with the resolution of around 10 microns, at the repetition rate of ms order.
This method was developed about 15 years ago by T. Maeno, and has been applied to various applications world wide. At NICT (former CRL), there are high resolution, transient, 3-D, portable, mountable and open PEA systems. We welcome students from universities, and some innovative PEA systems have been developed by them at NICT.
This method was developed about 15 years ago by T. Maeno, and has been applied to various applications world wide. At NICT (former CRL), there are high resolution, transient, 3-D, portable, mountable and open PEA systems. We welcome students from universities, and some innovative PEA systems have been developed by them at NICT.
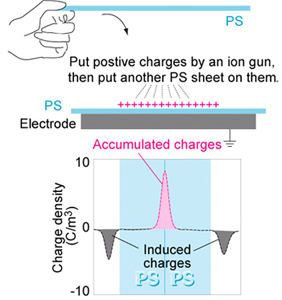
[Charge sandwich] This is the simplest example of the charge measurement. When you put some charges between two polystyren sheets, the charges stay there because polystyren is a kind of good insulation. Without voltage application, only induced charges are observed on the both electrodes due to the accumulated charges ih the middle. If you apply dc electric field from outside, surface charge quantity changes but the charges in the middle don't. |
 |
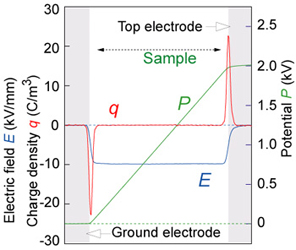 |
[Induced charge due to dc bias; Q=CV] When dc 5 kV is applied to a PS film sample, surface charges appear on the both electrodes. Electric field and potential distribution can be calculated easily from the observed charge distribution. |
|
|
|
|
|
-- Works introduced in this website has been done at NICT. --
(Last Update: August, 2004)